|
A bioassay determines the impact of a certain substance on living
organisms. You can use a bioassay to examine substances, such as
"compost tea" from a Decomposition Column,
to determine if they influence plant growth.
You can also test household substances such as sugar and coffee.
At what concentration are your seeds most affected?
Materials
- four black film cans with lids
- water twenty drops or about 2 mm of a solution to test
- eight to ten seeds of a small, fast-germinating plant, such
as turnips, Chinese cabbage, or Fast
Plants
- eye dropper or thin soda straw four paper towel wicks 1 cm
x 4 cm
| 1. |
Label four film cans 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and
CONTROL. |
|
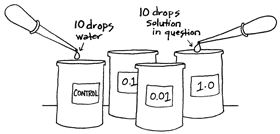 |
| 2. |
Add ten drops plain water to can labeled
CONTROL. Add 10 drops of the test solution to film can
labeled 1.0. |
|
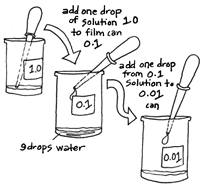 |
| 3. |
Add nine drops of water EACH to film cans labeled
0.1, and 0.01. Add one drop of full strength substance from
1.0 film can to can labeled 0.1. Mix. Take one drop of 0.1 strength
solution and add to can labeled 0.01. Mix well after each addition. |
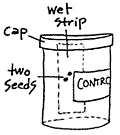
| 4. |
Insert one wick strip and two seeds into
each can as described in germination chamber. Cover with
cap. |
|
 |
Observe germination over the next 12 hours to 5 days. Graph how
the varying concentrations of your test substance affect a specific
response, such as germination rate. What other organisms can you
use for a bioassay? What other substances can you test?
|